The initial signs of hair thinning or loss can be unsettling. It’s that moment of sudden realization, looking in the mirror and questioning what’s changed. That feeling of unease is perfectly understandable, and naturally, many turn to the internet for answers.
However, the online world is awash with misinformation, from dubious home remedies to exaggerated claims of miracle hair growth products. Sorting fact from fiction can be a challenge.
That’s why we’ve created this guide, to debunk common hair loss myths and provide you with scientifically-backed solutions primarily focusing on hair loss in men.
Whether you’re just noticing the first signs or have been dealing with hair loss for some time, we’re here to help.
Debunking Common Hair Loss Misconceptions
Before exploring effective solutions, it’s crucial to address and dispel some of the most prevalent myths. By separating fact from fiction, we can establish a solid foundation for understanding hair loss and its management.
Myth #1: Wearing Hats Causes Hair Loss

A common misconception is that wearing hats leads to hair loss. This belief likely stems from the idea that head coverings ‘suffocate’ the scalp. However, hair follicles receive oxygen from the bloodstream, not the surrounding air.
Therefore, wearing hats, even daily, will not cause hair to fall out. It’s advisable, though, to avoid excessively tight hats that could cause scalp irritation over prolonged periods.
Myth #2: Hair Loss Only Affects Men
While male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) is most common in men, women also experience hair loss. Women often see diffuse thinning across the scalp, influenced by hormonal changes like pregnancy or menopause, and conditions such as PCOS or thyroid imbalances.
Tight hairstyles can also cause hair loss in women as well as men (traction alopecia).
Although this article primarily focuses on male pattern baldness, women should also seek professional advice for hair loss.
Myth #3: Hair Loss Is Always Genetic

Genetics does play a significant role in hair loss, but it’s not the sole determining factor.
Nutritional deficiencies, stress, scalp conditions, medical treatments like chemotherapy, and hormonal imbalances can also contribute to thinning hair or bald spots.
If hair loss occurs suddenly or in patches, consulting a specialist is recommended to rule out any underlying medical conditions. Specialized hair restoration clinics such as Gro Clinics offer personalized treatments, including transplants and non-surgical options, tailored to individual needs.
Myth #4: Shampoos and Serums Can Regrow Hair Overnight
The idea of shampoos and serums delivering rapid hair regrowth is appealing, but unrealistic.
While certain shampoos and scalp products can support scalp health and reduce hair breakage, they are not miracle cures. Be cautious of advertisements promising significant regrowth within short timeframes.
Genuine hair regrowth is a gradual process, often taking several months, and depends on addressing the root cause of the hair loss. Look for products containing ingredients like caffeine, biotin, ketoconazole, or saw palmetto, but understand that these provide support rather than a cure.
Myth #5: All Hair Loss Is Permanent

A common misconception is that once hair is lost, it’s gone forever. While certain types of hair loss, such as male pattern baldness, can be progressive, not all hair loss is permanent.
Conditions like telogen effluvium, which is often triggered by stress or hormonal changes, and alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition, can sometimes result in hair regrowth with appropriate treatment.
It is important to have a professional diagnosis to determine the type of hair loss and the potential for regrowth.
With these common misconceptions addressed, we can now turn our attention to evidence-based strategies for promoting hair regrowth and managing hair loss effectively.
Evidence-Based Solutions for Hair Regrowth
Having addressed common misconceptions, let’s explore scientifically supported solutions for promoting hair regrowth and managing hair loss, as used by professionals in the field. Here are some of the most common medical treatments:
1. Topical Minoxidil
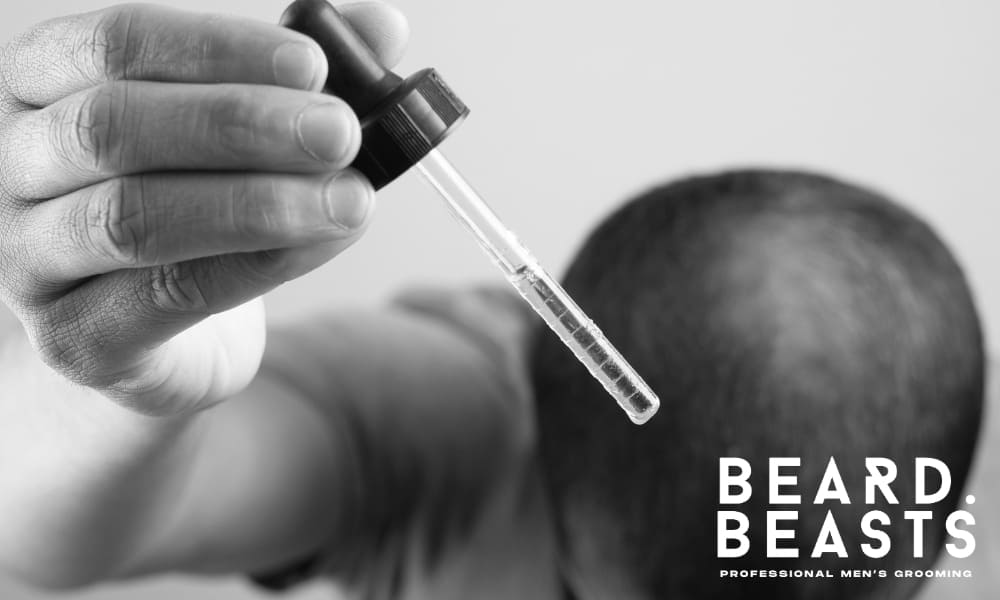
Topical minoxidil is a readily accessible, over-the-counter treatment that stimulates hair follicles by increasing scalp blood flow. Applied directly as a liquid or foam, it typically requires consistent use for at least 3 to 6 months to observe noticeable results, though individual responses vary.
Importantly, any regrowth achieved with minoxidil is often lost if usage is discontinued.
Consulting a healthcare professional is recommended to determine if minoxidil is appropriate for your specific situation and to ensure proper application.
2. Prescription Medications
Finasteride, commonly known as Propecia, is a prescription medication primarily prescribed for men. It operates by reducing dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair loss.
Consulting a general practitioner or hair loss specialist is recommended to determine its suitability for individual cases of male pattern baldness.
3. Hair Transplants
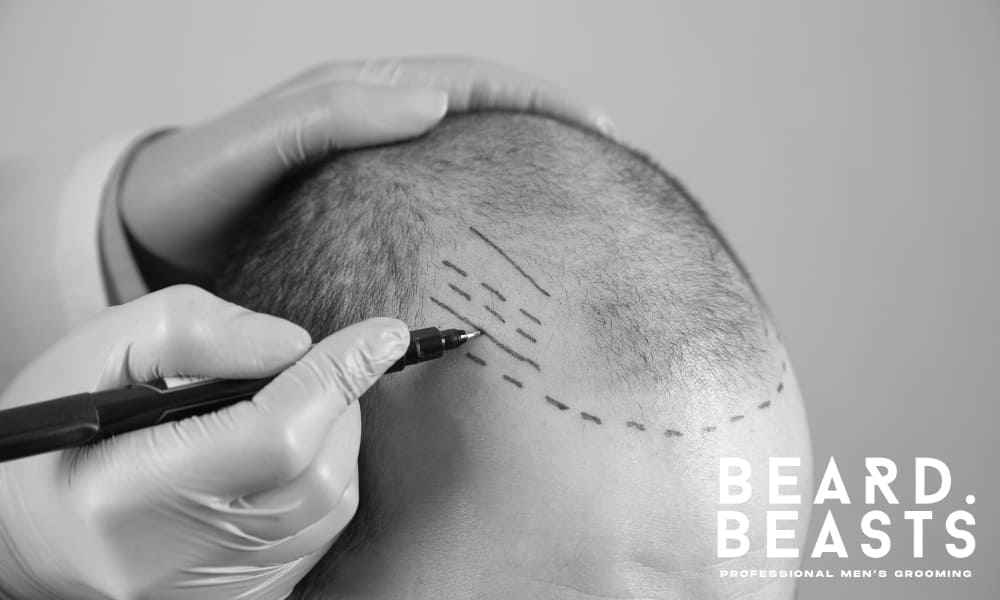
Modern hair transplant techniques offer natural-looking results by precisely transferring individual hair follicles from a donor area to thinning or bald regions.
Procedures like FUT and FUE allow for meticulous follicle placement, mimicking natural hair growth patterns. While hair transplants are a significant investment and involve a surgical procedure, they provide permanent results when performed by experienced surgeons.
A consultation is essential to assess candidacy and discuss realistic expectations.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is an innovative treatment where concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood are injected into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles and promote healing.
Often combined with other treatments, PRP has shown promise, especially for early hair loss. Multiple sessions are typically needed, and results vary. Consult a specialist to determine suitability.
5. Laser Therapy
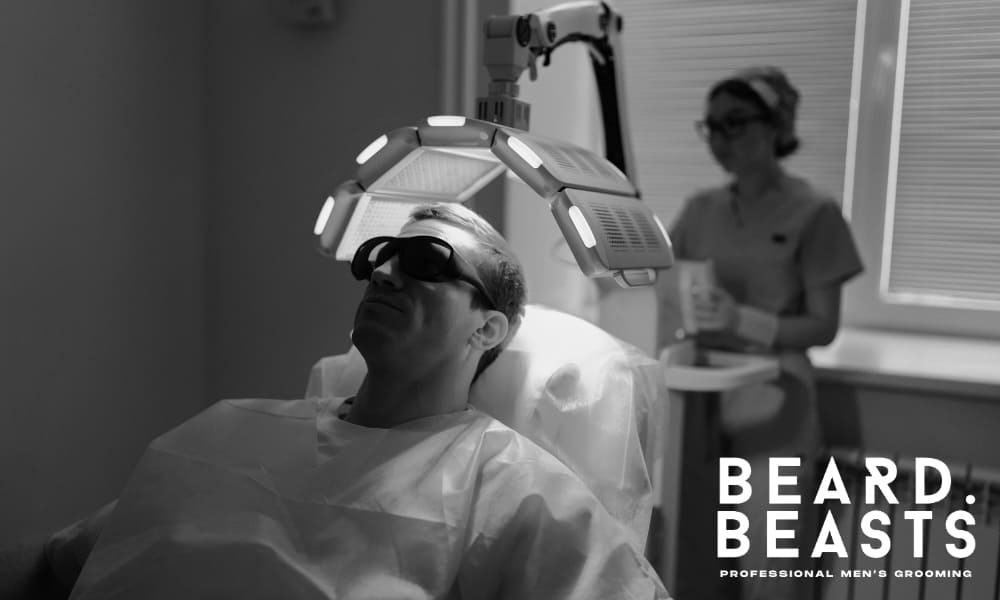
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is a non-invasive treatment that utilizes light to stimulate hair growth. Available in cap or comb devices, LLLT can be administered at home or in a clinical setting.
While ongoing research continues to explore its efficacy, some users report experiencing thicker and healthier hair with regular use.
6. Lifestyle Modifications
Internal factors significantly influence hair health.
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including iron, zinc, vitamin D, and protein, is crucial. Addressing chronic stress and anxiety is also vital, as these conditions can contribute to hair loss.
Additionally, consistent sleep patterns, aiming for 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night, and regular scalp massages can improve blood flow and potentially stimulate hair growth. Maintaining a consistent and appropriate hair care routine is also essential.
Conclusion:
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, but understanding the realities behind common myths and exploring evidence-based solutions can significantly alleviate anxiety and promote informed decision-making. While the internet offers a wealth of information, it’s crucial to distinguish between reliable information and myths.
Remember that genuine hair regrowth requires time and a tailored approach, often involving a combination of treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Consulting with a qualified dermatologist or hair loss specialist is essential for personalized guidance and to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
By embracing a proactive approach and relying on scientific evidence, individuals can effectively navigate hair loss and work towards achieving healthier, fuller hair.
Disclaimer: At Beard Beasts, we’re all about helping men look and feel their best — but we’re not doctors. The information provided in this article is for educational and grooming guidance purposes only. Always speak with a licensed healthcare provider before starting any hair loss treatments or making changes to your routine.





